All estimates can be consulted in more detail in our interactive online applications:
Projections of years lived with disability for 33 causes of illness
1. Key messages
- By 2040, the burden due to reduced quality of life will rise by 10% if current trends continue.
- Morbidity in women continues to rise at a higher pace compared to the rise among men.
- The existing Regional differences among the Brussels Capital Region, the Walloon Region and the Flemish Region remain stable up to 2040.
- The position of Belgium among EU-14 countries worsens from the 7th position in 2021 to the 5th position in 2040.
2. Prevalence and Years Lived with Disability
By 2040 morbidity in Belgium will go up by 10% if trends continue
By 2040, the burden due to reduced quality of life measured in Years Lived with Disability (YLDs) in Belgium is projected to go up by 10% for the 33 key diseases considered in the Belgian national Burden of Disease study. This number has been adjusted for the shifts in the population structure including age and population numbers based on the projected population estimates from the federal planning bureau.
- Age-adjusted YLDs
- Crude YLDs
Age-adjusted Years lived with disability by region, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
Crude Years lived with disability by region, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
When considering the number of reported diseases in Belgium, the current projections show an increase from 1 reported disease per person in 2021 to 1.2 reported diseases per person in 2040 after adjusting for changes in the age structure of the population. This indicates that multimorbidity, i.e., having several diseases simultaneously, might become a more urgent problem by 2040 in Belgium. When not correcting for a change in the age structure of the population, the number of diseases increases to 1.3 reported diseases per person by 2040.
- Age-adjusted prevalence
- Crude prevalence
Age-adjusted prevalence of all causes by region, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
Crude prevalence of all causes by region, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
The projected burden rises faster in women compared to men
The increase in disease burden due to a reduction in quality of life between 2021 and 2040 is projected to be higher in women (+18%) compared to men (+14%). In Belgium, the number of reported diseases in women might increase to 1.3 per 100,000 women by 2040, while in men, the number of reported diseases is estimated to go up to 1.1 per 100,000 men by 2040.
- Age-adjusted prevalence
- Crude prevalence
Age-adjusted prevalence of all causes by sex, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
Crude prevalence of all causes by sex, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
When looking at the YLDs, we see that the total YLDs caused by the 33 considered disease will become higher among women compared to the burden among men by 2040. In contrast, the number of reported diseases has been higher among women since the beginning of our measurements. This indicates that the increase in diseases with a higher impact on quality of life is bigger among women compared to men.
- Age-adjusted YLDs
- Crude YLDs
Age-adjusted Years lived with disability by sex, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
Crude Years lived with disability by sex, 2013-2040
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
The projected morbidity burden is similar across the three regions
The projected increase in burden is similar across the three regions in Belgium, with a 10% increase in both the Brussels Capital Region and Walloon Region, and a 9% increase in the Flemish Region. This suggests that the existing regional pattern - where the Walloon Region has the highest morbidity, followed by the Brussels Capital Region, and then the Flemish Region - will remain unchanged through 2040.
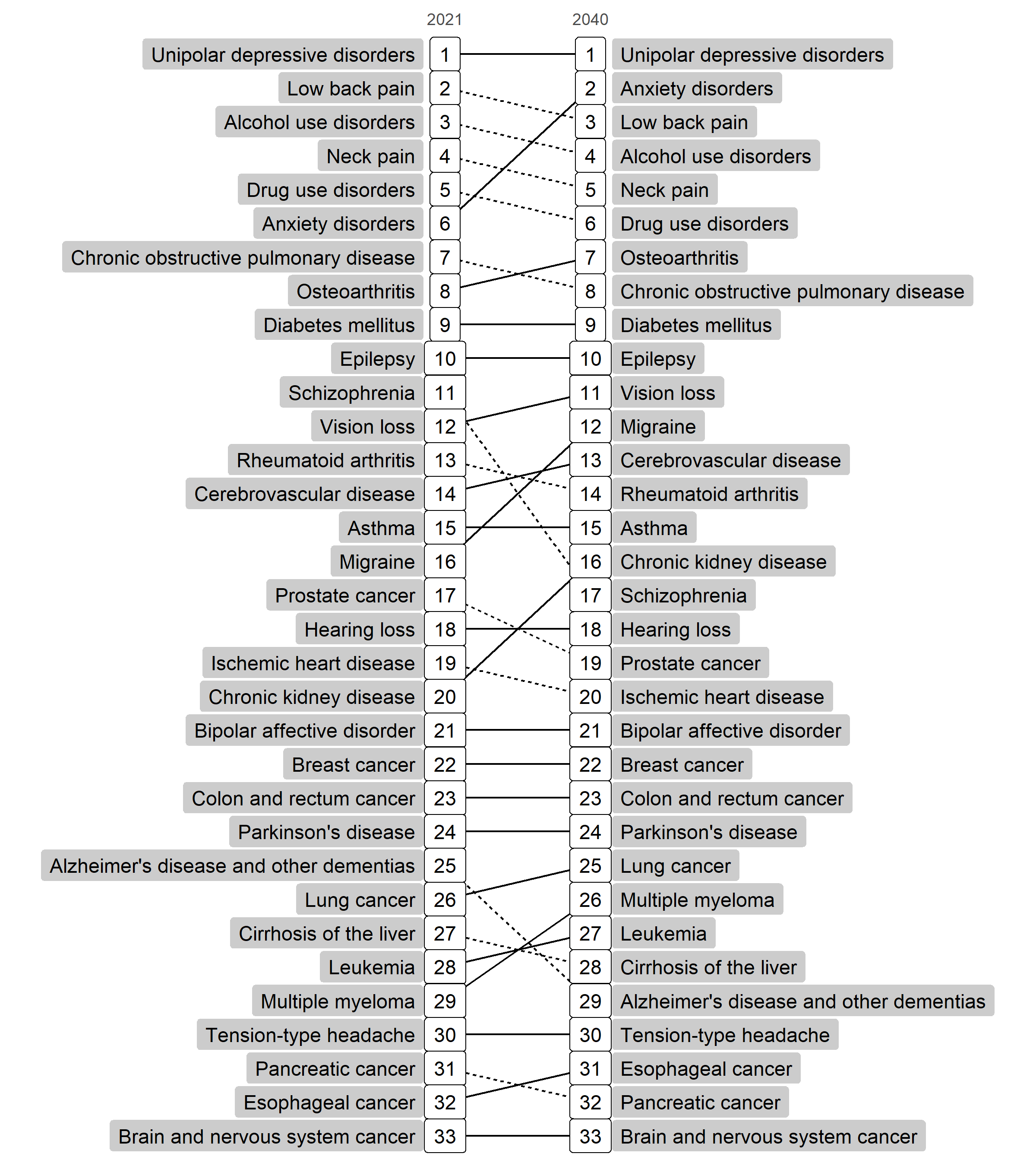
Mental health, musculoskeletal disorders and chronic respiratory disorders remain the largest contributors to morbidity in Belgium
By 2040, the disease groups that cause the heaviest disease burden in Belgium remain mental health, musculoskeletal disorders and chronic respiratory disorders. Although the overall morbidity burden rises in Belgium, there are some important differences in rankings of individual diseases between 2021 and 2040. Anxiety disorders show the highest projected increase from position 6 in 2021 to position 2 by 2040. Besides anxiety disorders, migraine and chronic kidney diseases also increase going up with at least two positions in the ranking.
Source: Own calculations based on the IMA, Intego, ERA, HIS, and Belgian Cancer Registry [1-5]
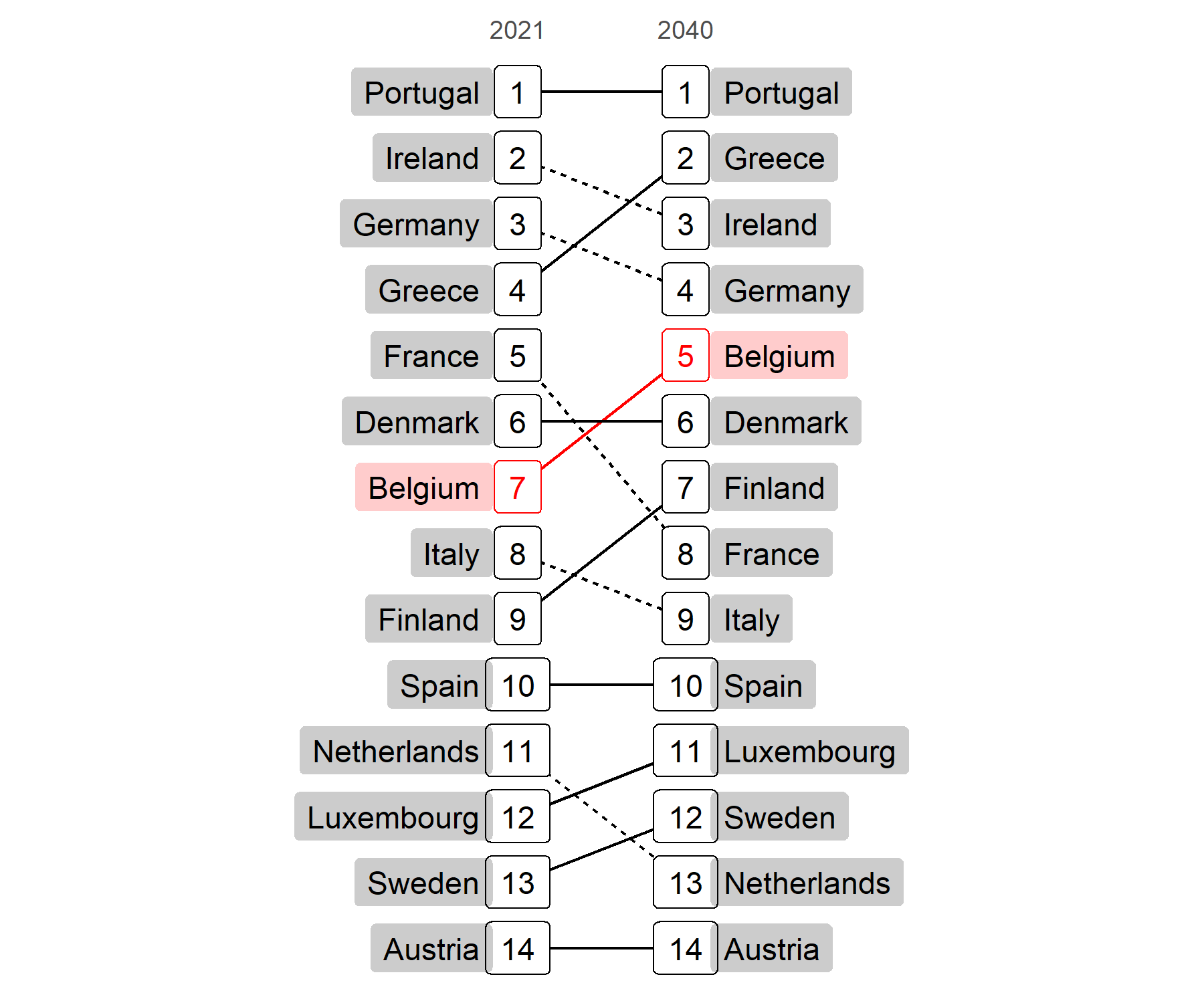
Prospects for Belgium among EU-14 countries are worse compared to other countries
In 2021, Belgium was ranked as the 7th country for age-adjusted YLDs caused by non-communicable diseases. According to the GBD Foresight study, the position of Belgium will worsen compared to other EU countries, since Belgium will rank 5th among the EU-14 in 2040.
3. Read more
Belgian Burden of Disease projections visualization tool
Belgian national burden of disease study. Methodological framework for the projections of the non-fatal burden of disease of non-communicable diseases in Belgium.
Background
What are the most important diseases in Belgium? Which risk factors contribute most to the overall disease burden? How is the burden of disease evolving over time, and how does it differ across the country? In the context of increasing budgetary constraints, a precise answer to these basic questions is more than ever necessary to inform policy-makers.
To inform healthcare planning and address future needs, Sciensano is conducting projections on the burden of disease in Belgium. By generating estimates of future prevalence and Years Lived with Disability (YLD) across different age groups, sexes, and regions, we can anticipate how patterns of morbidity may evolve over time. YLD projections quantify the impact of various diseases in terms of years lived with disability, while prevalence estimates indicate the number of individuals who may be affected. Together, these metrics provide a forward-looking assessment of health challenges likely to affect Belgium, helping to prioritize interventions and allocate resources more effectively.
We calculate disease burden estimates by age, sex and region, allowing for a very detailed assessment of the state of health. The complete set of estimates can be explored via https://burden.sciensano.be/shiny/projections.
Definitions
- Projections
- Projections refer to a methodology to predict the future via statistical analysis. In the current projections, the scenario assumes a continuation of the trends that have been observed in the past. To project the future non-fatal burden, a Bayesian generalized linear regression model was applied to the observed data, and the past trend was extrapolated into the future.
- YLD
- The Years Lived with Disability or YLDs in short is a measure of the non-fatal disease burden in a specific population. YLDs are calculated by multiplying the number of prevalent cases with the (severity-weighted) disability weight, which reflects the relative reduction in quality of life lost due to living with the disease.
- EU-14
- The EU-14 corresponds to all countries that belonged to the European Union between 1995 and 2004: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, and Sweden. We compare the Belgian health status to the EU-14 because these countries have similar socioeconomic conditions. Note: The United Kingdom is omitted since they have left the EU.
References
- Intermutualistic Agency (IMA). https://aim-ima.be/
- Intego, KU Leuven. https://intego.be/
- Renal Database, European Renal Association (ERA). https://www.era-online.org/en/registry/
- Health Interview Survey (HIS), Sciensano. https://www.sciensano.be/en/projects/health-interview-survey
- Belgian Cancer Registry (BCR). https://kankerregister.org/
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Results. Seattle, United States: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), 2020. Available from http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool
- Federal planning bureau
Please cite this page as: Sciensano. Burden of disease: Projections to 2040, Health Status Report, 19 Dec 2024, Brussels, Belgium, https://www.healthybelgium.be/en/health-status/burden-of-disease/projections